| Medically reviewed by
Robin Backlund, BHSc
Last update:

In the rhythm of life’s heartbeat, the strength of blood coursing through our veins often goes unnoticed.
This pressure, known as blood pressure, plays a pivotal role in our overall health.
High blood pressure, medically termed hypertension, is a condition that raises alarms for numerous health issues.
But what exactly constitutes high blood pressure? Let’s break it down.
Blood pressure is quantified in two numbers: the systolic and diastolic.
- The systolic number is the top reading and showcases the force of blood in your arteries when your heart beats.
- The diastolic, the bottom number, reflects the force when your heart is resting between beats.
To understand these readings, one needs to familiarize themselves with ‘mmHg’, which stands for millimeters of mercury. It’s the standard unit used worldwide to measure blood pressure.
While the term ‘normal blood pressure’ can vary slightly based on age and health, the guidelines provided by The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association categorize blood pressure readings as on a BP chart below.
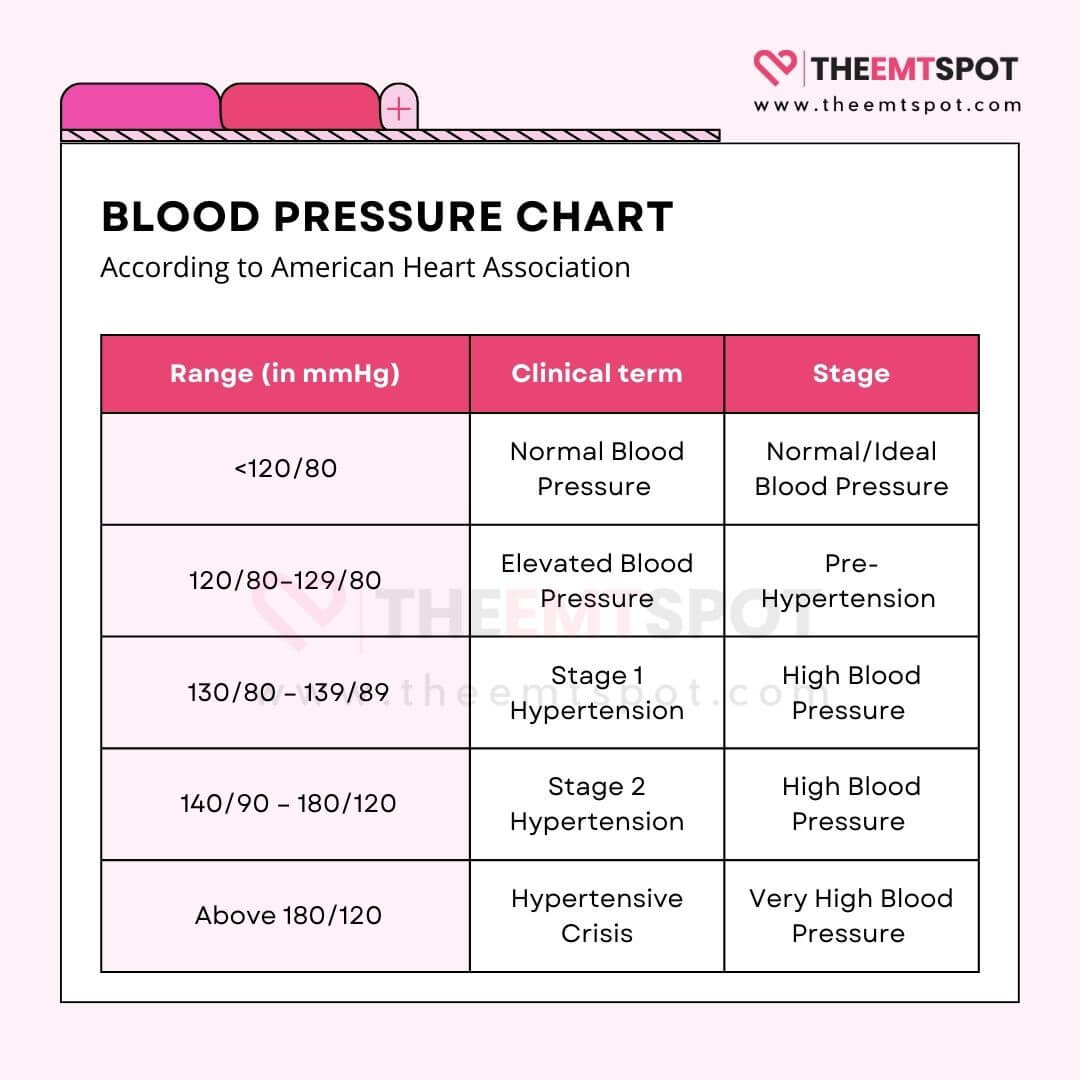
The primary symptom of hypertension often takes the form of a silent killer, as many individuals remain symptomless.
When symptoms do manifest, they might appear as headaches or shortness of breath.
The major risk factor is an unhealthy lifestyle, often combined with genetic predisposition.
As for the predominant cause, it often stems from a combination of genetics, age, and environment, with conditions like kidney disease playing a role.
According to a study titled “Combatting a Silent Killer – the Importance of Self-Screening of Blood Pressure from an Early Age,” published in the Experimental and Clinical Science journal in 2021, the incidence of hypertension is prevalent among adults of all ages, regardless of gender.
The best way to rule this out and seek appropriate medical treatment is by committing to routine blood pressure monitoring.
For diagnosing hypertension, doctors typically rely on multiple readings using a mercury-based sphygmomanometer, which later evolved into electronic devices commonly known as blood pressure monitors.
At-home blood pressure monitors have thus gained popularity. For those on the hunt for the best blood pressure monitor, Oxiline Pressure X Pro has consistently earned rave reviews for its accuracy and ease of use.
If diagnosed, the most common treatment approach is medication combined with lifestyle changes.
ACE inhibitors are one of the leading medications prescribed for hypertension.
But what if you wish to tread the natural path? Reducing sodium intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are pivotal in lowering high blood pressure naturally.
Contents
What are the types of high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Various types of hypertension are classified mainly into three categories:
- Systemic
- Local
- Severity index
While the systemic classification categorizes various forms of hypertension, the local category elucidates hypertension occurring across multiple body parts.
Lastly, the severity index is the one we are all familiar with, as it categorizes based on how severe and emergent your blood pressure level is.
Systemic hypertension
Systemic hypertension occurs when there is sustained elevated pressure in the arteries that transport blood away from the heart.
This condition arises when the force exerted by blood against the arterial walls remains elevated, leading to increased stress on both the heart and the blood vessels.
Various types of systemic hypertension are elaborated below.
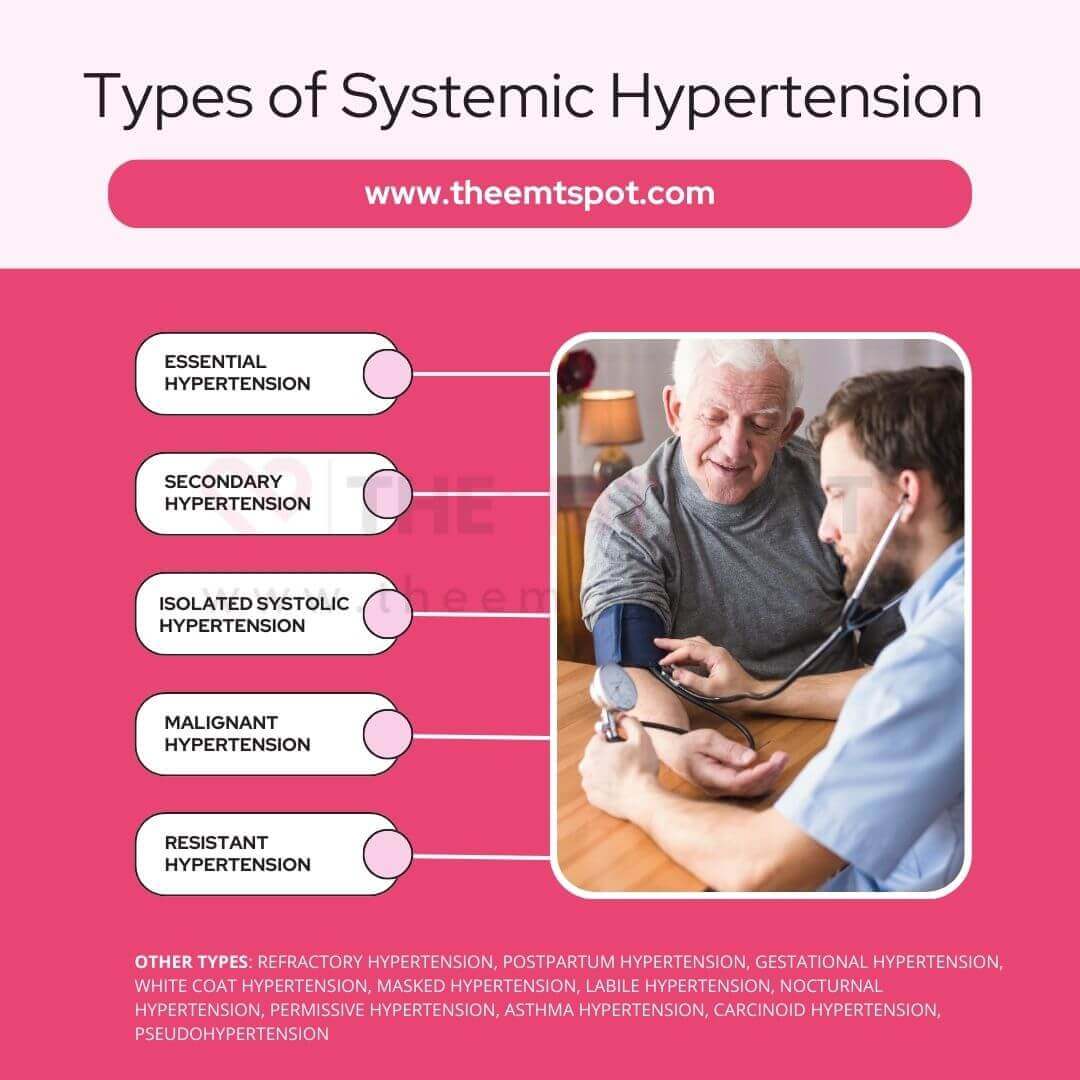
Essential or primary hypertension
Essential or Primary Hypertension is a condition of elevated blood pressure with no identifiable secondary cause, such as a different medical condition or medication.
The condition is characterized by systolic blood pressure values of 130 mmHg or more and/or diastolic blood pressure values of more than 80 mmHg.
According to a 2000 publication by a team of researchers from Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, Michigan, USA, it is the most prevalent type of hypertension, affecting 85% of those with high blood pressure.
Secondary hypertension
Secondary hypertension is when elevated blood pressure is caused by another medical condition or disease, such as kidney disease, adrenal disease, thyroid problems, or obstructive sleep apnea.
Secondary hypertension can manifest with extremely elevated blood pressure measurements, such as a systolic blood pressure exceeding 180 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure surpassing 120 mmHg.
Proper management and treatment of the underlying condition causing secondary hypertension can often control both the high blood pressure and the underlying disease.
Malignant hypertension
Malignant Hypertension (MHT) is a severe form of high blood pressure that damages the organs.
Malignant hypertension is typically characterized by extremely high blood pressure readings, commonly around 180/120 mmHg or higher.
A Nature review in the Journal of Human Hypertension by Dr. Domek and colleagues highlighted MHT as the most severe form of hypertension, emphasizing the clinical importance of understanding and managing this condition.
Isolated systolic hypertension
Isolated Systolic Hypertension (ISH) is a condition characterized by high systolic blood pressure (the top number when measuring blood pressure), specifically when it’s 130 mmHg or higher, while the diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number) remains below 90 mmHg.
In a study titled “Cardiovascular Risk of Isolated Systolic or Diastolic Hypertension in Young Adults”, published in the Circulation Journal, it is mentioned that ISH’s prevalence in young adults has been on the rise in recent years.
The association between ISH and cerebrovascular diseases like carotid atherosclerosis and stroke has been well-established, debunking earlier notions that ISH was a benign accompaniment of aging.
Resistant hypertension
Resistant hypertension is categorized as elevated blood pressure that persists above a desired threshold, even when three or more distinct types of antihypertensive medications are used simultaneously.
The resistant hypertension definition is blood pressure that stays high (140/90 millimeters of mercury or mmHg and above).
A study from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki has shown that common hypertensive drugs like doxazosin and bisoprolol are less effective for treating this disease, while drugs like spironolactone could be the best fit.
Refractory hypertension
Refractory hypertension is characterized by blood pressure that remains uncontrolled on maximal or near-maximal therapy, which includes the use of five or more antihypertensive agents of different classes.
The specific blood pressure range for refractory hypertension is not explicitly defined, but it is implied that the blood pressure remains uncontrolled despite aggressive treatment.
Additionally, an analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 1999 and 2014 found a prevalence of refractory hypertension of 0.5% among hypertensive individuals.
Postpartum hypertension
Postpartum Hypertension is a condition where the blood pressure of a woman remains higher than normal after childbirth.
The blood pressure is considered to be postpartum hypertension when the systolic pressure is 140 mmHg and the diastolic pressure is 90 mmHg or higher.
A study published in Current Obstetrics and Gynecology reports it impacts around 2% of pregnancies and persists for up to six weeks postpartum, encompassing individuals with deteriorating hypertension.
Preeclampsia (gestational hypertension)
Preeclampsia is a serious blood pressure condition that develops during pregnancy, characterized by a new onset of hypertension and either proteinuria or significant end-organ dysfunction, typically presenting after 20 weeks of gestation or postpartum.
The specific blood pressure range for diagnosing preeclampsia may vary, but it involves new-onset hypertension during pregnancy.
A research article published by Prof. Mayrink and colleagues in the Scientific World Journal noted that the global impact of preeclampsia was 4.6% across 40 countries.
White coat hypertension
White Coat Hypertension is when blood pressure taken at a medical setting is higher than that recorded at home, usually due to the stress of the doctor’s visit or the presence of healthcare professionals in white coats.
While the exact blood pressure range for White Coat Hypertension can differ, it is defined by elevated blood pressure during clinical assessments while maintaining normal blood pressure outside these situations.
According to a study published in Hypertension in AHA journals, it is essential to study the effect of white coat hypertension in younger populations rather than just in elders, as it could be beneficial in preventing unnecessary medication in younger patients.
Masked hypertension
Masked hypertension is marked by an individual having higher blood pressure in their daily life or common surroundings than during medical appointments, potentially causing a delay in diagnosing and treating hypertension because it falsely appears as normal blood pressure.
According to a journal publication in AHA Hypertension, an office blood pressure average lower than 130/80 mmHg, contrasted with an average awake ambulatory blood pressure or home blood pressure of 130/80 mmHg or greater, shall be considered as masked hypertension.
A study by Cohen et al., published in the Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich), has identified masked hypertension as a very prevalent and unexplored condition among hypertensive patients.
Labile hypertension
Labile Hypertension refers to a scenario where a person’s blood pressure repeatedly or suddenly changes from normal to abnormally high levels, often during stressful situations.
It can abruptly fluctuate from being abnormally high, approximately 140/90 mmHg or over, and return to its normal range.
According to Dr. Swan and the team’s publication in an AHA journal, stress management, a low-sodium diet, and comprehensive medication are the best possible ways to regulate this condition.
Nocturnal hypertension
Nocturnal hypertension is defined as high blood pressure experienced at night, specifically with a nighttime blood pressure equal to or greater than 120/70 mmHg, as per the older guidelines, or greater than 110/65 mmHg, as per the newer 2017 ACC/AHA guidelines.
According to a 2018 study from Jichi Medical University School of Medicine, a clinic and morning home reading of <130/80 mmHg shall be counted as masked nocturnal hypertension.
According to Dr. MB, MRCPI, every 10 mmHg rise in nighttime blood pressure was associated with adverse cardiovascular consequences such as stroke.
Permissive hypertension
Permissive hypertension is a method that involves deliberately allowing elevated blood pressure levels to persist following a stroke.
This approach entails reducing a patient’s antihypertensive medication for a period of 24-48 hours after a stroke because maintaining higher blood pressure during this timeframe can serve as a protective measure.
For individuals with a significant increase in blood pressure, it is recommended to aim for a 15% reduction in blood pressure within the initial 24 hours after the stroke occurs.
In a publication by a team of doctors from Duke University Medical Center, it was noted that permissive hypertension could potentially serve as a substitute for cerebrospinal fluid drainage in critical surgical procedures.
Asthma hypertension
Asthma and hypertension are known to coexist more frequently than would be expected by chance.
The blood pressure range in individuals with both asthma and hypertension can vary based on numerous factors, including the severity of each condition, the effectiveness of treatment, and other individual health factors.
A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology identified that hypertension and asthma are correlated, such that asthma patients are highly likely to have high blood pressure.
Carcinoid hypertension
Carcinoid syndrome arises from a systemic secretion of humoral factors like polypeptides, biogenic amines, and prostaglandins, typically from well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, formerly known as carcinoid tumors.
In certain situations, especially under the stress of surgery and anesthesia, individuals with carcinoid syndrome can experience hypertensive crises, which might be referred to as Carcinoid Hypertension.
The blood pressure range in Carcinoid Hypertension is not specified, but it’s implied that blood pressure would be significantly elevated during a carcinoid hypertensive crisis.
Pseudohypertension
Pseudohypertension occurs when blood pressure readings are falsely elevated, typically due to the loss of flexibility in the arterial walls or calcification of the blood vessels, which cannot be compressed.
This condition is more common in elderly, diabetic, and uremic individuals and is also known as pseudohypertension in the elderly, non compressibility artery syndrome, and Osler’s sign of pseudohypertension
According to Dr. Messerli, MD, and his team from Ochsner Clinic in LA, atheromatosis or lipid deposition in arteries could lead to pseudohypertension, which is characterized by varying blood pressure readings on the cuff versus the actual pressure within the arteries.
Local hypertension
Local hypertension is the elevated blood pressure in specific areas or systems of the body rather than throughout the entire circulatory system.
Wherever an artery connects to an organ, there is a risk of high blood pressure localized to that area. One common example is renal hypertension or high blood pressure in the arteries carrying blood to the kidney.
However, different types exist, and each of them is explained below.

- Portal hypertension: Elevated blood pressure within the portal venous system, often due to liver cirrhosis. Can lead to varices and ascites.
- Pulmonary hypertension: Elevated pressure within the pulmonary arteries, potentially leading to stress on the right ventricle of the heart. The underlying factors can be either of unknown origin (idiopathic) or associated with other medical conditions.
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure without a known cause. Often presents with headache and may affect vision.
- Epididymal hypertension: Also known as “blue balls,” it’s a temporary discomfort in the testicles due to prolonged sexual arousal without release.
- Ocular hypertension: Elevated intraocular pressure without signs of glaucoma. Increases the risk of developing glaucoma.
- Postural hypertension: A misnomer. Typically referred to as postural hypotension, drop in blood pressure upon standing leading to dizziness.
- Renovascular hypertension: Elevated blood pressure caused by narrowing of the blood vessels that carry blood to the kidneys.
- Venous hypertension: Increased blood pressure within the venous system. Can lead to varicose veins, edema, and ulcers.
- Pediatric hypertension: High blood pressure in children. Causes can be primary or due to underlying conditions. Early detection and management are crucial.
- Reactive pulmonary hypertension: A response to another condition, such as heart or lung disease, causing elevated pulmonary artery pressure.
Severity index
This is a quantitative classification of hypertension based on the blood pressure readings associated with various symptoms.
This classification helps clinicians have a numerical reference to the severity of a patient’s heart health. Generally, it is classified into four categories, as explained below.
1. Stage 1 Hypertension
- Systolic blood pressure: 130-139 mmHg
- Diastolic blood pressure: 80-89 mmHg
2. Stage 2 Hypertension
- Systolic blood pressure: 140 mmHg or higher
- Diastolic blood pressure: 90 mmHg or higher
3. Hypertensive urgency
Hypertensive urgency refers to very high blood pressure that doesn’t currently show signs of severe organ damage but requires rapid blood pressure reduction.
It typically involves systolic blood pressure above 180 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure above 120 mmHg.
Urgent treatment is needed to lower blood pressure within hours or a few days to prevent complications.
4. Hypertensive emergency (or crisis)
A hypertensive emergency, also known as a hypertensive crisis, is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition.
It involves a significant and rapid increase in blood pressure, often with systolic blood pressure over 180 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure over 120 mmHg.
A hypertensive emergency requires immediate medical attention, typically in an emergency room or hospital setting.
It can lead to organ damage, such as stroke, heart attack, kidney failure, or damage to blood vessels.
While there could be different types of hypertension that could exist, the symptoms of most systemic versions are almost similar. The next section will provide a brief overview of them.
What are the symptoms and signs of high blood pressure (hypertension)?
High blood pressure symptoms are often not visible or expressive. This is why this particular condition is dubbed the ‘silent killer.’ Many people with hypertension are unaware they have it.
However, when blood pressure is significantly elevated, some individuals may experience symptoms and signs, which can be explained below.
- Headaches: Severe headaches, especially in the back of the head, can sometimes occur.
- Breathing difficulty: Difficulty with breathing, including shortness of breath, can arise, especially during physical activity or exertion.
- Nosebleeds: Frequent or severe nosebleeds can be a sign of high blood pressure in some cases.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy can happen, especially when standing up quickly.
- Chest pain: Pain or discomfort in chest can occur if high blood pressure leads to heart problems.
- Vision changes: Blurred vision or changes in vision can be associated with hypertension in some cases.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or fatigued more often than usual may be a symptom, although it is nonspecific.
- Palpitations: Some individuals may feel their heart beating irregularly or strongly.
- Nausea or vomiting: High blood pressure can occasionally cause nausea or vomiting.
- Confusion or cognitive changes: Severe hypertension may affect cognitive function, leading to confusion, memory problems, or difficulty concentrating.
- Chest discomfort: Besides chest pain, some people with hypertension may experience chest discomfort, pressure, or a feeling of fullness in the chest.
- Facial flushing: Redness or flushing of the face can occur, particularly in individuals with extremely high blood pressure.
- Swelling: Swelling or edema in the legs, ankles, feet, or other parts of the body can be a sign of uncontrolled hypertension affecting the kidneys.
- Sleep disturbances: Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or frequent waking during the night, may be linked to high blood pressure.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus) can be associated with severe hypertension.

Symptoms could be evident or silent due to the nature of this disease, but the risk factors leading to it need careful evaluation and possible prevention. A thorough discussion of risk factors and causes of hypertension is included below.
What are the risk factors and causes of high blood pressure (hypertension)?
The major risk factors and hypertension causes shall mostly be attributed to your lifestyle. However, many other risk factors are elaborated by WHO and the American Heart Association.
A group of researchers from Harvard Medical School, in their 2023 publication in the JAMA journal, has identified lifestyle and diet as major risk factor which affects women more than men.
Meanwhile, a study published in 2023 in Cures, authored by Prof. Meher, confirms that people who smoke, chew tobacco, drink alcohol, and are obese have double the risk of hypertension.
More than a dozen factors could influence blood pressure, and all the major risk factors and causes of hypertension are explained below.
Genetics
Genetic makeup can predispose individuals to hypertension. Specific genes affecting blood vessel function and salt balance play roles in blood pressure regulation.
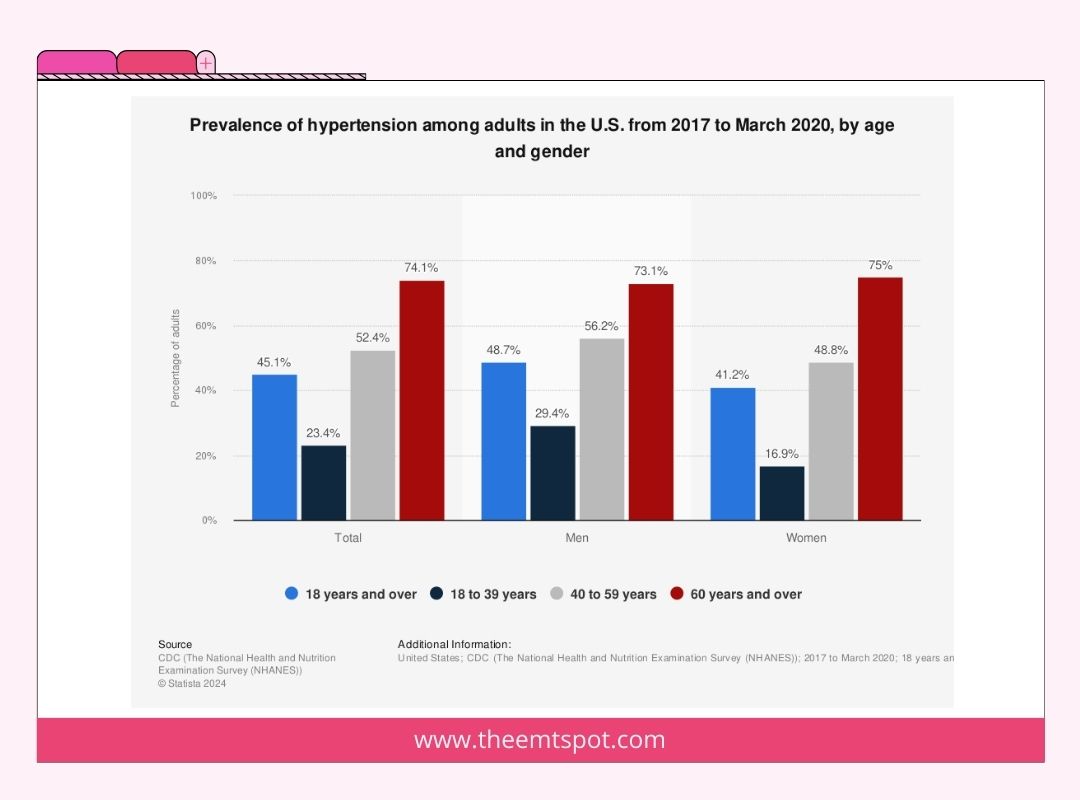
Age
The risk of hypertension increases as individuals age due to various physiological changes. As people age, arteries may harden and lose elasticity, leading to increased blood pressure.
Family history
Having a family history of hypertension significantly increases one’s risk. Inherited genetic factors from parents to their offspring can make individuals more susceptible to developing high blood pressure.
Ethnicity
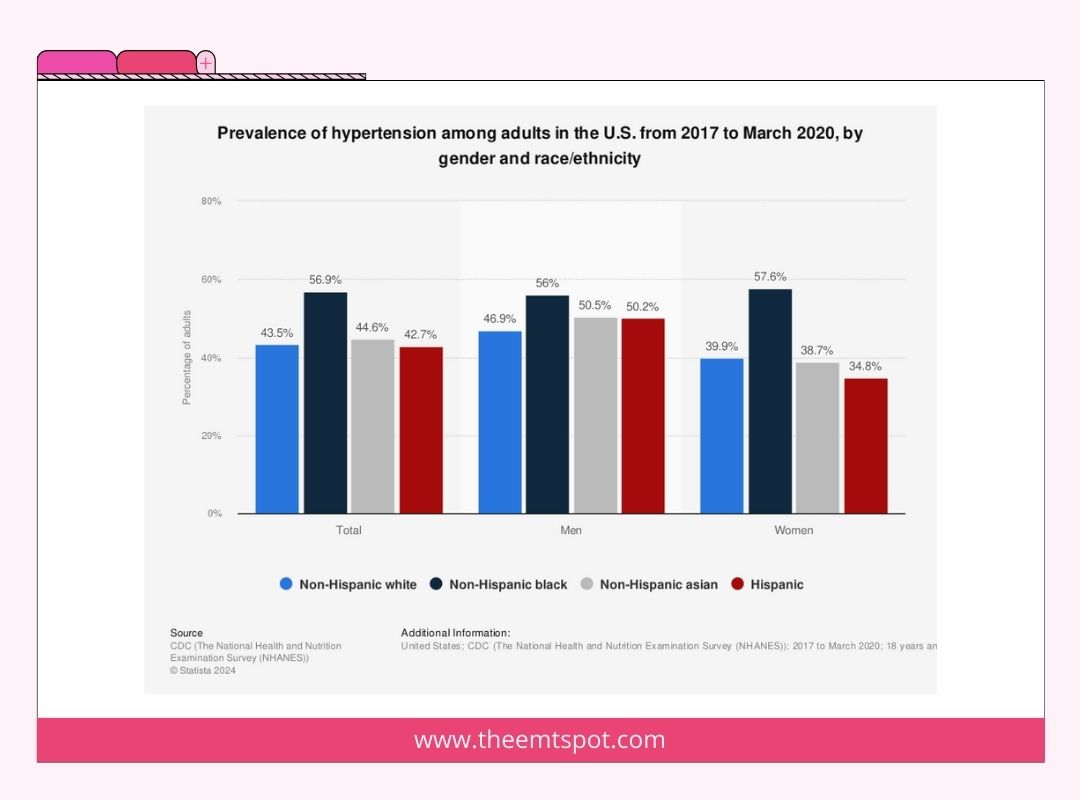
Specific ethnic populations face an elevated risk of hypertension. For instance, research indicates that African-American adults have a greater likelihood of developing hypertension in comparison to individuals from other racial or ethnic backgrounds.
Childhood factors
Early-life conditions such as poor nutrition or exposure to toxic substances can lead to hypertension later in life. Additionally, childhood obesity is a strong predictor of adult hypertension.
Environmental factors
Exposure to pollutants, high-stress environments, or living in areas with limited access to healthy food can contribute to the development of hypertension. Lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity also play crucial roles.
Socioeconomic status
Low socioeconomic status can contribute to hypertension due to limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, and safe spaces for exercise. The stress associated with financial instability can also elevate blood pressure.
Occupational risks
Jobs with high-stress levels or exposure to harmful substances can increase the risk of hypertension. Long working hours and sedentary workstyle are other occupational risks.
Poor diet
Consuming a diet that is rich in sodium, processed foods, and saturated fats can can elevate your hypertension. In contrast, a well-rounded diet abundant in fruits, greens, cereals, grains and lean proteins can regulate it.
Lack of exercise
Engaging in consistent physical activity aids in weight management, reducing the risk of elevated blood pressure. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity, which is a notable factor associated with hypertension.
Stress
Chronic stress can lead to behaviors that increase the risk of hypertension, like poor diet and lack of exercise. Additionally, stress may cause a temporary spike in blood pressure, and prolonged stress may contribute to long-term hypertension.
Obesity
Obesity strains the heart, requiring it to pump more blood and increasing the pressure on arterial walls, which can lead to hypertension. It’s also often associated with other risk factors like high cholesterol and diabetes.
High cholesterol
High cholesterol leads to atherosclerosis, a condition that narrows and hardens arteries, increasing blood pressure. Managing cholesterol levels is crucial for preventing hypertension and related cardiovascular diseases.
Diabetes
Diabetes can damage arteries, making them targets for hypertension. Both conditions share risk factors like obesity and an unhealthy diet, which often co-occur, and each can worsen the other, making management and treatment more challenging.
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is marked by interruptions in breathing while asleep, has the potential to cause elevated blood pressure. The body releases stress hormones in response, which can elevate blood pressure.
Hormonal imbalances
Imbalances in hormones, particularly those involved in fluid regulation and blood pressure control like aldosterone, can contribute to hypertension. Hormonal disorders like hyperthyroidism can also lead to high blood pressure.
Coexisting conditions
Having multiple health conditions, like diabetes and high cholesterol, can worsen hypertension or make it more difficult to manage, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive healthcare approach.
Medications
Certain medications, including some over-the-counter drugs and prescriptions like corticosteroids or birth control pills, can raise blood pressure. It’s crucial to monitor blood pressure levels when starting any new medication and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Dietary supplements
Some dietary supplements, especially those containing licorice root, ephedra, or bitter orange, can elevate blood pressure. It’s essential to exercise caution before using supplements, particularly for individuals with pre-existing hypertension.
Pregnancy (Gestational Hypertension)
Gestational hypertension occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves post-delivery. It’s a temporary condition but requires monitoring as it can progress to preeclampsia, a severe condition endangering both the mother and fetus.
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, like Cushing’s syndrome or pheochromocytoma, can cause hypertension by disrupting hormone regulation of blood pressure. Early diagnosis and treatment of these conditions are critical for managing blood pressure.
Thyroid disorders
Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can lead to hypertension. The thyroid gland is vital in regulating metabolism and energy expenditure, and any dysfunction can impact blood pressure regulation.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to hypertension, among other health issues. It’s advised to limit alcohol intake to moderate levels to manage blood pressure effectively and promote overall cardiovascular health.
Tobacco
Tobacco use, whether smoking or chewing, can cause immediate and long-term elevation in blood pressure. The chemicals in tobacco can damage arterial walls, leading to narrower arteries and higher blood pressure.
Caffeine
Caffeine leads to a temporary spike in blood pressure, especially in people who are sensitive to caffeine or who do not consume it regularly. While its long-term effects on blood pressure are still debated, it’s advisable for hypertensive patients to limit it.
What is the relationship between salt intake and hypertension?
The relationship between consumption of salt and hypertension is well-established and backed by a multitude of scientific investigations.
The primary concern with high salt intake is that it causes the body to retain water, which in turn increases blood pressure.
Furthermore, high salt intake can impair the function of blood vessels and lead to arterial stiffness, which is another pathway to hypertension.
It has been understood that lowering salt intake can reduce blood pressure, and it is frequently suggested as a lifestyle change for individuals with hypertension or prehypertension.
It’s important to note that not everyone is equally sensitive to salt, and some individuals are more predisposed to the blood pressure-raising effects of high salt intake than others.
In a 2015 study published in the AHA journal Hypertension, it was demonstrated that reducing salt intake could not only lower blood pressure but also reduce the risk of obesity.
This study, along with others, highlights the potential benefits of dietary salt reduction for managing blood pressure and preventing hypertension.
In the upcoming section, you will learn how hypertension is diagnosed so that patients can keep track of it.
What are the diagnosis and tests for high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Diagnosing high blood pressure (hypertension) typically involves a range of tests and procedures to ensure accurate measurement and to identify any underlying conditions or risk factors.
The WHO has published a literature titled “Guideline for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults”‘ to establish standardized treatment protocols for adults with hypertension. The basic strategy is outlined below.
Blood pressure measurement
- Sphygmomanometer: Blood pressure is most commonly measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer. This can be done at a healthcare provider’s office, a pharmacy, or at home.
- 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM): This method entails using a portable blood pressure monitor for a full day, capturing blood pressure readings at different intervals throughout both day and night.
- Home blood pressure monitoring: Frequent tracking of blood pressure at home through the use of a digital blood pressure monitor.
Physical examination
A keen physical examination by doctor to check for signs of heart disease, kidney disease, or other underlying conditions that could cause hypertension.
Laboratory tests
- Blood tests: Testing of cholesterol levels, blood sugar, kidney function, and other indicators of heart disease risk.
- Urine tests: Testing of kidney function and signs of kidney disease.
Imaging tests
- Echocardiogram: To check for heart abnormalities and evaluate heart function.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys: To check for kidney abnormalities.
Additional testing
Depending on initial findings, additional tests may be conducted, such as renal function tests, hormonal tests, or other specialized testing to identify or rule out underlying conditions.
Risk assessment
Assessing the patient’s risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including family history, diet, physical activity level, and other lifestyle factors.
These tests and examinations help healthcare providers gain a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s cardiac health. However, do you know how this is treated in a clinical scenario? The next section will elaborate on that.
What are the treatments for high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Treating high blood pressure necessitates a comprehensive approach that often includes medication, lifestyle alterations, and, at times, additional medical interventions.
Medication options include drugs like Thiazide diuretics (reduce blood volume), ACE inhibitors (block hormone for narrowed vessels), ARBs (inhibit hormone for narrowed vessels), Beta-blockers (lower heart rate), Calcium channel blockers (relax vessels), and Renin inhibitors (reduce blood pressure).
On the other hand, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing hypertension.
Adopting a heart-healthy diet like the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which is characterized by its low sodium and saturated fat content, along with an abundance of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can be beneficial.
Moreover, engaging in regular physical exercise, managing weight, limiting alcohol intake, reducing sodium in the diet, and quitting smoking are all vital lifestyle changes that can contribute to lower or controlled blood pressure.
Furthermore, additional medical interventions like regular blood pressure monitoring both at home and during doctor’s visits are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Stress management employing meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can also be instrumental in managing hypertension by alleviating stress.
Treating conditions like sleep apnea, which often coexists with hypertension, can significantly contribute to lowering blood pressure.
In a 2013 study titled “Effectiveness of Yoga for Hypertension: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” by Marshal Haggins, it was clarified that yoga and similar meditation techniques could significantly reduce blood pressure levels, especially in hypertensive patients.
The natural approach to regulating hypertension has become popular, and there are a few more of these approaches elaborated on in the next part.
What medications are used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Treatment for high blood pressure often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
Medications may be prescribed to lower blood pressure when lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient. Some of the major classes are explained below.
- Diuretics (Water Pills): Eliminate excess sodium and water to lower blood volume and pressure. Examples: thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics.
- ACE Inhibitors: Block angiotensin II, relaxing blood vessels. Examples: lisinopril, enalapril, captopril.
- ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers): Inhibit angiotensin II, leading to vessel relaxation. Examples: losartan, valsartan, irbesartan.
- Beta Blockers: Slow heart rate and reduce contractions to lower blood pressure. Examples: metoprolol, atenolol, propranolol.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Block calcium entry to relax vessels. Examples: amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil.
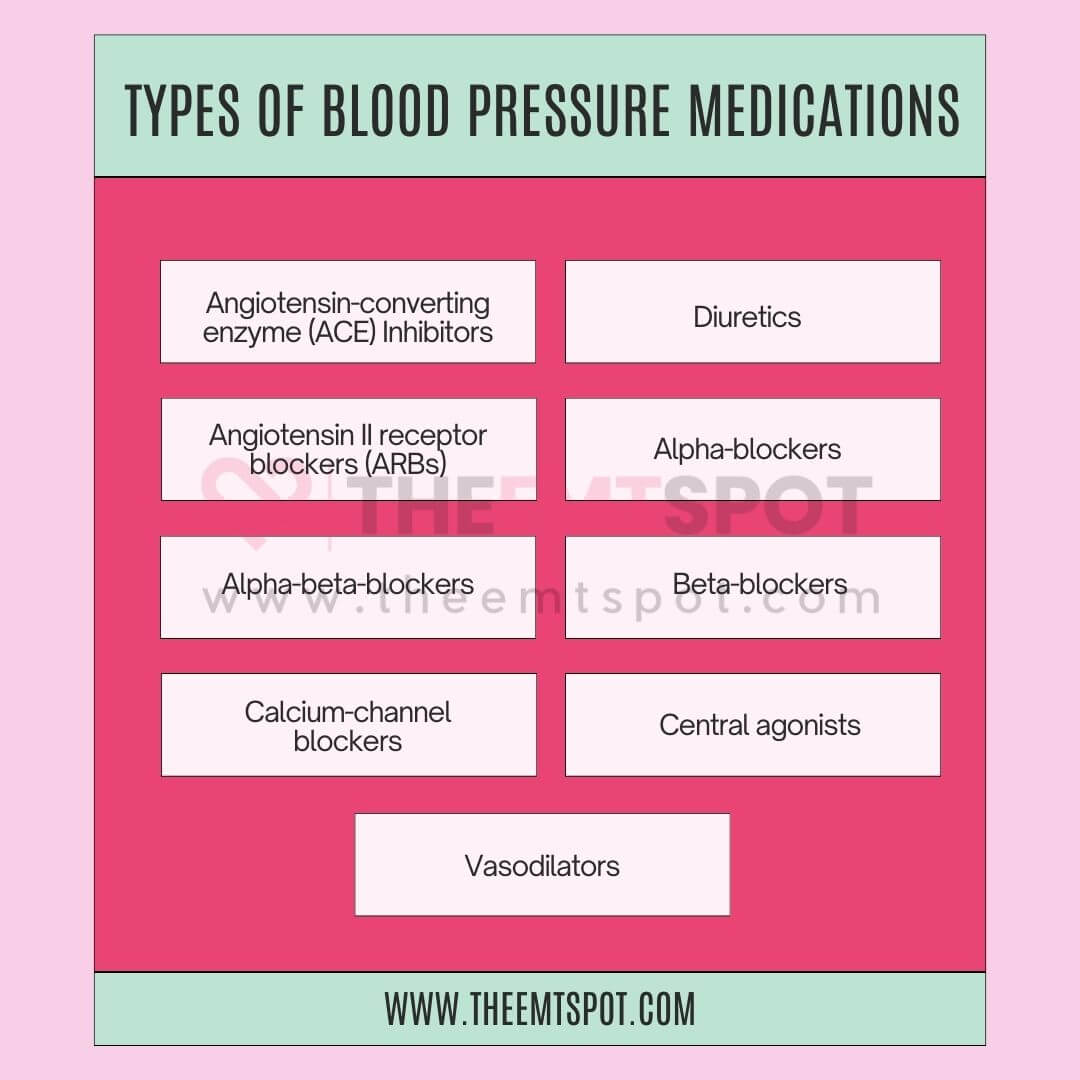
The list of medications for high blood pressure is extensive because the condition varies from individual to individual, and therefore, it requires a tailored approach for effective treatment.
Blood pressure medications are generally safe and effective, but they can have side effects. Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, headache, and gastrointestinal issues like constipation.
Some medications can lead to cough, elevated potassium levels, or kidney problems. Others may cause swelling in the extremities or a slow heart rate. These side effects vary depending on the type of medication and individual response.
This is why alternative therapy has emerged as a contemporary solution for treating hypertension, and it is gaining popularity.
How do you lower high blood pressure naturally?
To lower blood pressure naturally, it mainly involves making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits.
Luke Laffin, MD, Medical Director of Cardiac Rehabilitation, shares that:
“There is good data to back up a variety of lifestyle measures that we can use to naturally lower blood pressure. They become the cornerstone of hypertension management.”
According to him:
“70% is lifestyle, 30% is medications. I can give you six, seven, eight blood pressure medicines. If you’re not doing the lifestyle components, you’re really not going to be effectively lowering your blood pressure”
… thereby highlighting the importance of lifestyle change.
From his interview and AHA guidelines, below are 15 steps to naturally lower hypertension.
- Reduce your salt intake: Excess salt can raise blood pressure, so aim to consume less salt in your diet.
- Eat healthy foods: Incorporate a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid refined carbs and sugar: Minimize the consumption of refined carbohydrates and added sugars in your diet.
- Try the DASH diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes foods that can help lower blood pressure.
- Drink water: Maintaining proper hydration is crucial for overall well-being and can contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure.
- Eat some dark chocolate: Dark chocolate in moderation, may have a positive effect on blood pressure due to its antioxidants.
- Try these herbs: Some herbs like garlic, basil, and cinnamon may have blood pressure-lowering properties.
- Consider taking vitamins and supplements: Consult with a healthcare professional about supplements like potassium, magnesium, and fish oil.
- Manage weight: Losing excess weight can significantly lower blood pressure.
- Reduce stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in physical activity most days of the week, which can help lower blood pressure.
- Limit alcohol intake: Consuming alcohol in moderation or abstaining from it entirely can have a positive impact on blood pressure.
- Get good sleep: Aim for quality sleep to support overall health and blood pressure regulation.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use can elevate blood pressure, making it imperative to quit for the sake of heart health.
- Cut back on caffeine: Excessive caffeine consumption may contribute to higher blood pressure, so monitor your intake.
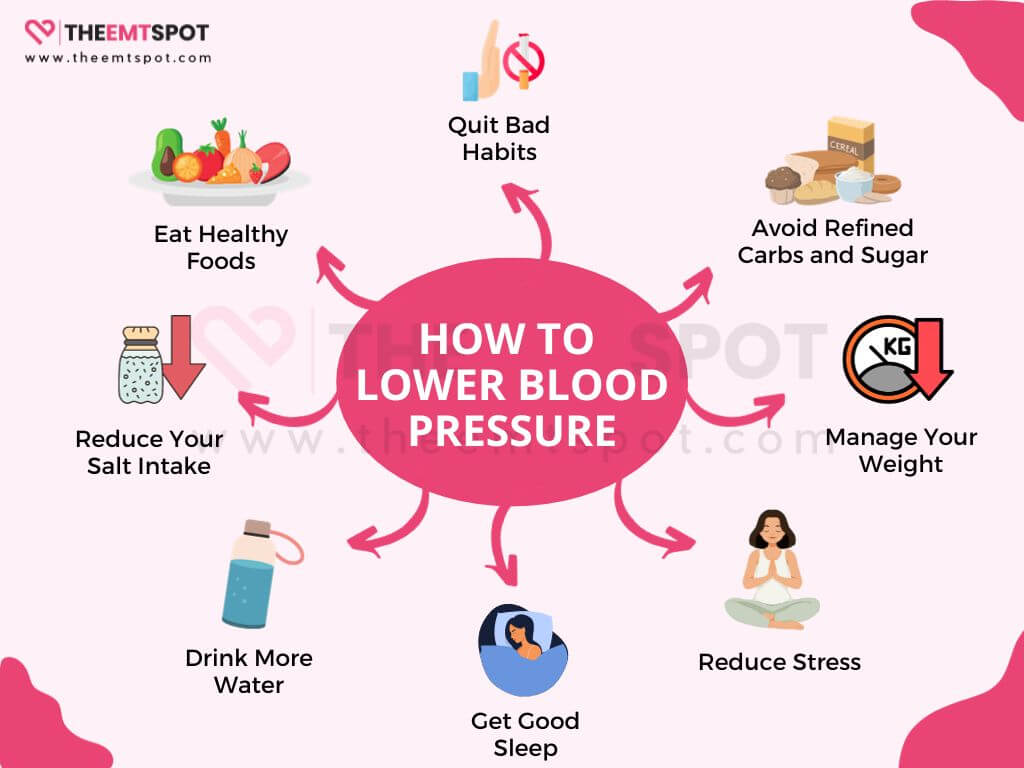
Natural approaches encompass a vast list, among which weight loss is a significant step that can significantly lower your blood pressure. The next section will discuss the importance of weight management.
What role does weight management play in hypertension control?
Weight management plays a pivotal role in the control of hypertension (high blood pressure). It brings forth several significant advantages for blood pressure regulation.
According to the AHA, weight management is one of the best natural approaches for reducing hypertension, and there are various reasons for it.
Shedding excess weight can lead to a notable reduction in blood pressure levels, with even modest weight loss making a meaningful impact.

Also, weight loss contributes to the improved functioning of blood vessels, reducing resistance and enhancing their efficiency in regulating blood flow, a crucial aspect of hypertension management.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight eases the stress on the heart, as it diminishes the additional workload required for pumping blood throughout the body.
Furthermore, weight management is closely linked to a decreased risk of developing other health conditions often associated with hypertension, such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
These conditions can further contribute to elevated blood pressure, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
For those individuals with hypertension who are on medication, effective weight management can enhance the drugs’ efficacy, potentially allowing for lower medication doses.
What is the best diet for high blood pressure (hypertension)?
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is frequently suggested as an excellent dietary plan for controlling high blood pressure.
This diet is specifically crafted to reduce blood pressure and enhance cardiovascular health by guiding food choices.
A study by Prof. Matthew J. Belanger and colleagues, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found that the DASH diet had significantly lowered the biomarkers of cardiac damage compared to a typical American diet.
Below are a few dietary changes you can include in your routine.
- High in fruits and vegetables: The DASH diet emphasizes consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. These food items contain ample amounts of potassium, which aids in mitigating the impact of sodium on blood pressure.
- Whole grains: It encourages whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat bread, and whole grain pasta over refined grains, which are higher in fiber and nutrients.
- Lean proteins: The diet includes lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes (beans, lentils, and peas) while limiting red meat and processed meats.
- Low-fat dairy: It incorporates low-fat or fat-free dairy products, which are sources of calcium and protein without the added saturated fat of full-fat dairy.
- Nuts, seeds, and legumes: The DASH diet includes nuts, seeds, and legumes as sources of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Limited sweets and added sugars: It restricts sugary beverages and sweets, reducing the intake of added sugars.
- Reduced sodium: The DASH diet is lower in sodium (salt) compared to the typical American diet. Reducing sodium intake is crucial for blood pressure control.

What alternative therapies effectively manage hypertension?
Alternative therapies to manage hypertension include approaches that are different from clinically prescribed or suggested approaches.
According to a publication by Richard Nahas, MD, CCFP, in the CFP MFC journal, alternative therapies have been found effective, and the review suggests that they should be studied further to check for efficacy. A few of the popular approaches are elaborated below.
- Herbal supplements: Consider herbal remedies like hibiscus tea, garlic, or hawthorn extract (consult a healthcare provider before use).
- Acupuncture: Some people find acupuncture sessions beneficial for stress reduction and blood pressure management.
- Biofeedback: Biofeedback techniques can help individuals learn to control physiological responses, potentially lowering blood pressure.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): Participate in MBSR programs, which combine meditation and yoga for stress reduction.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): CoQ10 supplements may have a modest blood pressure-lowering effect (consult a healthcare provider before use).
- Aromatherapy: Aromatherapy with essential oils like lavender may help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
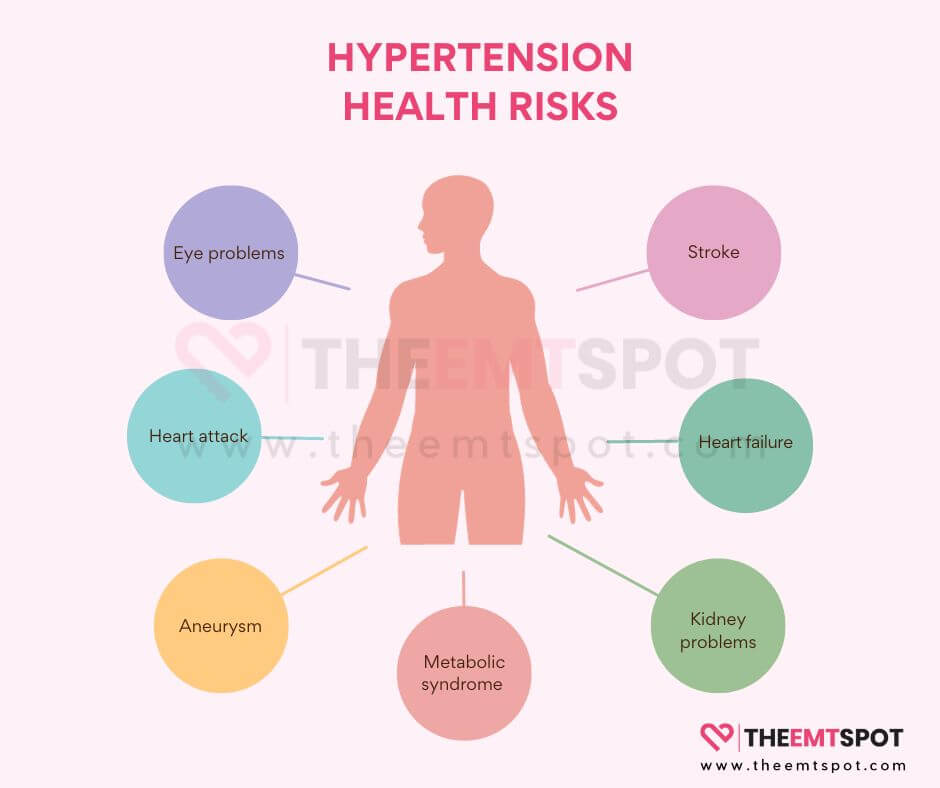
What problems does high blood pressure (hypertension) cause?
High blood pressure (hypertension) can cause several problems, especially to various organs.
Since the effects are not always prominent, the damage becomes evident only when the situation worsens. Some of the potential issues are explained below.
- Heart attack (Myocardial Infarction): Persistent high blood pressure can result in the narrowing and stiffening of the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
- Stroke (Cerebrovascular Accident): Elevated blood pressure has the potential to harm the blood vessels within the brain, thereby raising the likelihood of a stroke.
- Aneurysm: High blood pressure can result in vascular wall weakening, increasing the risk of aneurysm formation. An aneurysm is a blood vessel bulge that, if it ruptures, can cause serious internal bleeding.
- Heart failure: High blood pressure causes the heart to work harder to pump blood against increased resistance in the arteries. Over time, this extra workload can lead to the heart muscle thickening and becoming less efficient.
- Kidney problems: The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. Chronic hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste and excess fluid from the body.
- Eye problems (Retinopathy): Hypertension can damage the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition called hypertensive retinopathy. This can result in vision problems and even blindness if left untreated.
- Metabolic syndrome: Hypertension is often associated with other risk factors, such as obesity, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Changes with memory or understanding: Chronic hypertension may have adverse effects on the brain, increasing the risk of cognitive impairment, vascular dementia, or Alzheimer’s disease.
But do you know how hypertension affects your heart if you don’t pay much attention to it? The section below will help you understand that.
How does hypertension affect the heart over time?
Hypertension affects the heart by gradually exerting significant strain over time, leading to several adverse effects. Initially, the heart has to work harder to pump blood against elevated pressure in the arteries.
This extra workload can cause the heart muscle to thicken (left ventricular hypertrophy), reducing its efficiency in pumping blood.
As hypertension persists, the arteries that supply the heart with oxygen and nutrients (coronary arteries) may become damaged and narrowed, increasing the risk of coronary artery disease and angina (chest pain).
Over the years, hypertension can also weaken the heart, weakening its ability to pump blood effectively.
According to an AHA editorial, persistent hypertension over an extended period can increase the risk of heart failure. When heart failure occurs, the heart becomes unable to meet the body’s demands for oxygen and nutrients.
Additionally, high blood pressure can contribute to the development of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. But does hypertension affect your mental health, like in the case of the heart?
Does high blood pressure influence cognitive health?
Yes, high blood pressure (hypertension) can significantly influence cognitive health.
According to an NIH -National Institute on Aging editorial article, observational research indicates that individuals who experience elevated blood pressure during midlife, typically spanning from their 40s to early 60s, face an elevated likelihood of experiencing cognitive deterioration in their later years.
Over time, uncontrolled hypertension can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the brain.
This vascular damage can lead to various cognitive impairments and an increased risk of dementia.
Hypertension results in decreased blood flow to the brain, depriving it of essential oxygen and nutrients.
This can lead to small areas of brain damage known as microinfarcts, which can accumulate over time and contribute to cognitive decline.
Additionally, hypertension is associated with an increased risk of developing conditions such as cerebral small vessel disease and white matter lesions, both of which are linked to cognitive impairment.
Furthermore, chronic hypertension can promote the development of Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia.
What are the challenges in managing hypertension in elderly individuals?
Managing hypertension in elderly individuals presents unique challenges due to age-related factors and comorbidities.
Firstly, elderly patients may have multiple chronic conditions, complicating treatment regimens. Medication interactions and the potential for adverse effects are concerns when addressing hypertension alongside other health issues.
Elderly individuals may also exhibit atypical symptoms or masked hypertension, making diagnosis and monitoring more complex.
Additionally, blood pressure goals may differ for older adults, as overly aggressive treatment can lead to hypotension and falls.
Treatment adherence can be challenging due to cognitive impairments, medication costs, and polypharmacy. Moreover, elderly patients may be more resistant to lifestyle changes.
Lastly, managing hypertension in the elderly requires a tailored approach, considering individual health status, frailty, and functional capacity.
Regular monitoring and adjustments are crucial as patients age and treatment goals evolve.
In sum, the multifaceted nature of aging and comorbidities necessitates a comprehensive and patient-centered approach to hypertension management in the elderly.
How to prevent hypertension?
Preventing hypertension may appear straightforward in theory, yet implementing it, particularly in our fast-paced modern lifestyle, can be a formidable task.
An article featured in the AHA journal Hypertension by Prof Paul K. Whelton et al. suggests several strategies that can be integrated into your daily routine to significantly lower the risk of developing hypertension.
- Eat a healthy diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce saturated fats and sodium intake.
- Limit sodium intake: Excess salt can raise blood pressure. Aim for less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day.
- Practice mindful eating: Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to help maintain a healthy weight and lower blood pressure.
- Keep a healthy weight: Maintain a body mass index (BMI) within the healthy range.
- Manage stress: Use stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Do not smoke: Smoking damages blood vessels and can lead to hypertension.
- Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure. Consume alcohol in moderation.
- Cut down on caffeine: High caffeine intake can temporarily elevate blood pressure.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Try natural supplements: Some supplements, like potassium and omega-3 fatty acids, may help manage blood pressure. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
- Get support: Seek social and emotional support to help manage stress and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
One of the major steps in prevention is to incorporate a routine monitoring habit into your daily life. Home blood pressure monitors are available for this purpose, and you will learn more about them below.
How to take blood pressure at home?
Taking blood pressure at home, especially with modern electronic monitors, is fairly easy. All you need is a reliable and accurate blood pressure monitor, and the rest of the steps are easy, as elaborated below.
- Choose a quality monitor: Invest in a reputable blood pressure monitor for accurate readings. The best monitors are typically digital and easy to use.
- Prepare: Sit in a comfortable, quiet place. Avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking for at least 30 minutes before measurement.
- Position yourself: Sit with your back straight, feet flat on the floor, and arm at heart level. Rest for a few minutes before taking the measurement.
- Apply the cuff: Place the cuff snugly on your bare upper arm, aligning it with your heart. Ensure it’s not too tight or too loose.
- Read the monitor: Start the monitor and remain still. It will inflate and deflate, displaying your systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) blood pressure readings.
- Record your reading: Note down the numbers, as well as the date and time. Repeat measurements at the same time daily for consistency.

If you need a reliable reading, it’s essential to use the best blood pressure monitor to eliminate false readings and ensure you always obtain clinically valid data. The section below will provide further insights.
What are the best blood pressure monitors?
The best monitors to check blood pressure that you can find in the current market will be either from the brands Oxiline or CheckMe. These two outperform other brands like QardioArm, Omron, and Withings.

In the Oxiline lineup, the best performance is offered by its smart monitor, Oxiline Pressure X Pro, which can easily connect to your smartphone via their app for seamless health data transfer.
On the other hand, the CheckMe BP2, with its futuristic design and lightweight, sleek construction, is one of the best portable smart monitors available in the market. A detailed comparison of both is provided below.
Pressure X Pro | CheckMe BP2 | |
 |  | |
Our rating | 4.9 | 4.7 |
Type | Cuffed with tube | Cuffed tubeless |
Smart feature(s) |
|
|
Number of users the device supports | Multi-User Suport via App | Multi-User Suport via App |
Number of readings per user |
|
|
Weight of the device | 453 g | 240 g |
PROMO CODE | EMTSPOT10 (10% OFF) | EMTSPOT15 (15% OFF) |
More in this topic






 Robin Backlund is a dedicated journalist and a medical student who has written several articles and essays exposing the falseness and hollowness of online resources in the medical science niche.
Robin Backlund is a dedicated journalist and a medical student who has written several articles and essays exposing the falseness and hollowness of online resources in the medical science niche.